Introduction: The Central Processing Unit (CPU) stands as the brain of a computer, orchestrating the millions of instructions per second that drive our digital experiences. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the intricate world of CPU architecture, shedding light on its fundamentals and how it significantly influences the overall performance of your computer system.
What is CPU Architecture?
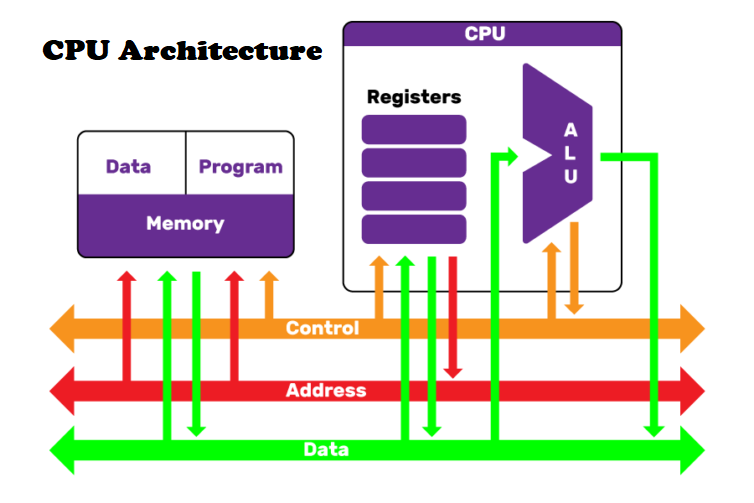
CPU architecture refers to the design and structure of a processor, encompassing various elements that enable it to execute instructions and perform computations. It comprises components like the Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU), Control Unit, Registers, Cache, and the CPU’s instruction set architecture (ISA).
Key Components of CPU Architecture
- Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU): The ALU handles mathematical calculations and logical operations, performing tasks like addition, subtraction, AND, OR, etc.
- Control Unit: Responsible for managing and coordinating the activities of the CPU, fetching instructions, decoding them, and controlling the flow of data within the processor.
- Registers: These are small, high-speed memory locations within the CPU used to store data temporarily during processing, enabling quick access for computations.
- Cache Memory: Acts as a high-speed buffer between the CPU and the main memory, storing frequently accessed data to expedite processing.
- Instruction Set Architecture (ISA): The ISA defines the CPU’s machine language, determining the set of instructions it can execute.
Absolutely! Here’s an SEO-friendly blog post on understanding CPU architecture:
Title: Explained: Understanding CPU Architecture and Its Impact on Computer Performance
Introduction: The Central Processing Unit (CPU) stands as the brain of a computer, orchestrating the millions of instructions per second that drive our digital experiences. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the intricate world of CPU architecture, shedding light on its fundamentals and how it significantly influences the overall performance of your computer system.
What is CPU Architecture?
CPU architecture refers to the design and structure of a processor, encompassing various elements that enable it to execute instructions and perform computations. It comprises components like the Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU), Control Unit, Registers, Cache, and the CPU’s instruction set architecture (ISA).
Key Components of CPU Architecture
- Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU): The ALU handles mathematical calculations and logical operations, performing tasks like addition, subtraction, AND, OR, etc.
- Control Unit: Responsible for managing and coordinating the activities of the CPU, fetching instructions, decoding them, and controlling the flow of data within the processor.
- Registers: These are small, high-speed memory locations within the CPU used to store data temporarily during processing, enabling quick access for computations.
- Cache Memory: Acts as a high-speed buffer between the CPU and the main memory, storing frequently accessed data to expedite processing.
- Instruction Set Architecture (ISA): The ISA defines the CPU’s machine language, determining the set of instructions it can execute.
Absolutely! Here’s an SEO-friendly blog post on understanding CPU architecture:
Title: Explained: Understanding CPU Architecture and Its Impact on Computer Performance
Introduction: The Central Processing Unit (CPU) stands as the brain of a computer, orchestrating the millions of instructions per second that drive our digital experiences. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the intricate world of CPU architecture, shedding light on its fundamentals and how it significantly influences the overall performance of your computer system.
What is CPU Architecture?
CPU architecture refers to the design and structure of a processor, encompassing various elements that enable it to execute instructions and perform computations. It comprises components like the Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU), Control Unit, Registers, Cache, and the CPU’s instruction set architecture (ISA).
Key Components of CPU Architecture
- Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU): The ALU handles mathematical calculations and logical operations, performing tasks like addition, subtraction, AND, OR, etc.
- Control Unit: Responsible for managing and coordinating the activities of the CPU, fetching instructions, decoding them, and controlling the flow of data within the processor.
- Registers: These are small, high-speed memory locations within the CPU used to store data temporarily during processing, enabling quick access for computations.
- Cache Memory: Acts as a high-speed buffer between the CPU and the main memory, storing frequently accessed data to expedite processing.
- Instruction Set Architecture (ISA): The ISA defines the CPU’s machine language, determining the set of instructions it can execute.
Types of CPU Architectures
- CISC (Complex Instruction Set Computing): CISC processors are designed to execute complex instructions directly, often resulting in fewer instructions needed to perform tasks.
- RISC (Reduced Instruction Set Computing): RISC processors focus on executing a smaller set of simpler instructions, aiming for faster execution times and greater efficiency.
Absolutely! Here’s an SEO-friendly blog post on understanding CPU architecture:
Title: Explained: Understanding CPU Architecture and Its Impact on Computer Performance
Introduction: The Central Processing Unit (CPU) stands as the brain of a computer, orchestrating the millions of instructions per second that drive our digital experiences. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the intricate world of CPU architecture, shedding light on its fundamentals and how it significantly influences the overall performance of your computer system.
What is CPU Architecture?
CPU architecture refers to the design and structure of a processor, encompassing various elements that enable it to execute instructions and perform computations. It comprises components like the Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU), Control Unit, Registers, Cache, and the CPU’s instruction set architecture (ISA).
Key Components of CPU Architecture
- Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU): The ALU handles mathematical calculations and logical operations, performing tasks like addition, subtraction, AND, OR, etc.
- Control Unit: Responsible for managing and coordinating the activities of the CPU, fetching instructions, decoding them, and controlling the flow of data within the processor.
- Registers: These are small, high-speed memory locations within the CPU used to store data temporarily during processing, enabling quick access for computations.
- Cache Memory: Acts as a high-speed buffer between the CPU and the main memory, storing frequently accessed data to expedite processing.
- Instruction Set Architecture (ISA): The ISA defines the CPU’s machine language, determining the set of instructions it can execute.
Types of CPU Architectures
- CISC (Complex Instruction Set Computing): CISC processors are designed to execute complex instructions directly, often resulting in fewer instructions needed to perform tasks.
- RISC (Reduced Instruction Set Computing): RISC processors focus on executing a smaller set of simpler instructions, aiming for faster execution times and greater efficiency.
Impact of CPU Architecture on Performance
- Speed and Efficiency: The architecture significantly influences a CPU’s speed and efficiency in processing instructions, affecting overall system performance.
- Power Consumption: Different architectures can affect power consumption, with some designs being more power-efficient than others.
- Multitasking and Parallel Processing: CPU architecture influences a processor’s ability to handle multiple tasks simultaneously (multitasking) and execute instructions in parallel (parallel processing).
Conclusion: Understanding CPU architecture is crucial for grasping how processors function and how they impact a computer’s performance. From the ALU to cache memory and the ISA, each component plays a vital role in executing instructions and processing data. Whether it’s the efficiency of instruction execution, power consumption, or multitasking capabilities, CPU architecture profoundly influences a computer’s capabilities and performance.
